dig output|10 Linux DIG Command Examples for DNS Lookup : Pilipinas Learn how to use the dig command in Linux and Unix for DNS lookup and query DNS name servers for various resource records. See syntax, options, examples, and output of the dig command for different query types . Get the best bonus by signing up and using the Sky Bet promo code. Codes are also available for: sport, casino, bingo and poker. . Once you make the qualifying wager, you will receive £40 (8 x £5) of free bets to use on Football markets. £40 in Free Football Bets When You Place a £10 Bet. Learn More Show Less.
dig output,dig offers a variety of options that allow you to customize your DNS queries extensively: +short: Simplifies the output to show just the answer. dig example.com +short .
1. In this command you're using @a.edu-servers.net server to resolve robot.cs.washington.edu sub-domain of washington.edu domain, however that doesn't mean .Learn how to use the dig command in Linux to query the DNS of a given server and retrieve information about domains and IPs. See examples of dig output and how to interpret it. Dig stands for domain information groper. Using dig command you can query DNS name servers for your DNS lookup related tasks. This article explains 10 examples on how to use dig command. 1. Simple dig Command .

Learn how to use the dig command in Linux and Unix for DNS lookup and query DNS name servers for various resource records. See syntax, options, examples, and output of the dig command for different query types . The dig command queries the DNS for information about domain names and their associated records, such as IP addresses, mail servers, and name servers. It is a valuable tool for diagnosing DNS issues and verifying . The dig command is an incredibly powerful tool for querying DNS records. Dig stands for Domain Information Groper and is the utility of choice for most DNS administrators working on Linux. It can be used to confirm DNS .dig outputdig (domain information groper) is a flexible tool for interrogating DNS name servers. It performs DNS lookups and displays the answers that are returned from the name server(s) that were .
The dig command is a DNS lookup utility that can be used to troubleshoot DNS issues in Linux. It can also be used to query DNS records. The dig command can be used to .dig output 10 Linux DIG Command Examples for DNS LookupIn a script I want to be able to write an IP address to somewhere easily, so I thought using dig (or a similar command) with back-ticks. However the simplest output I've been able to come up to wrt dig parameters is > dig -t A +noall +answer www.google.com www.google.com. 300 IN A 173.194.66.106 www.google.com. 300 IN A 173.194.66.104
dig (domain information groper) is a flexible tool for interrogating DNS name servers. It performs DNS lookups and displays the answers that are returned from the name server(s) that were queried. Most DNS administrators use dig to troubleshoot DNS problems because of its flexibility, ease of use and clarity of output. Other lookup tools tend to have less functionality than dig.Most DNS administrators use dig to troubleshoot DNS problems because of its flexibility, ease of use, and clarity of output. Other lookup tools tend to have less functionality than dig . Although dig is normally used with command-line arguments, it also has a batch mode of operation for reading lookup requests from a file.
10 Linux DIG Command Examples for DNS LookupIn the below example we add the +short option to the .digrc in our home directory and then perform a dig on google.com, we can see that the output confirms it was run with +short even though we did not specify it on the command line. [root@centos7 ~]# cat .digrc +short [root@centos7 ~]# dig google.com 216.58.220.110 Summarydig is a network administration command-line tool for querying the Domain Name System (DNS). dig is useful for network troubleshooting and for educational purposes. [2] . There are many output formatting options available. A common selection to make the output more terse is:
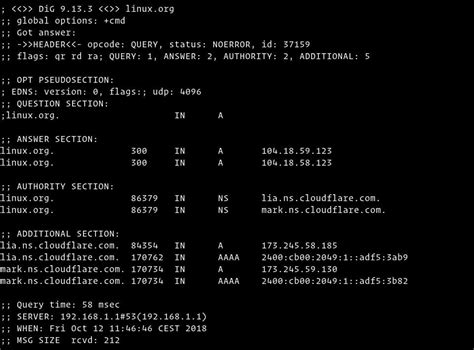
That it the basics of the dig command. Great, but if you don't understand the output you might as well use nslookup (sorry for the jab, nslookup is a fine tool). In the next section we will break down each line of the output. Understanding Dig Output. As we mentioned in the introduction, dig is a very powerful tool.
The result should look similar to the dig output we examined earlier in this guide: If you want to learn more about the dns command and what options you can use with Globalping, run globalping dns --help or check out our documentation. Using Dig Effectively. Dig is a versatile tool, and here are some tips for using it effectively:

Dig is a very powerful Linux command to query DNS in Linux. We will dive into the dig command output today. The dig command is a DNS lookup utility that can be used to troubleshoot DNS issues in Linux. It can also be used to query DNS records. The dig command can be used to perform a number of different tasks, including: Querying a single DNS . Where, +nocmd – Toggles the printing of the initial comment in the output identifying the version of dig and the query options that have been applied. This comment is printed by default. +noall – Set or clear all display flags. +answer – Display [do not display] the answer section of a reply. The default is to display it. +ttlid – Display [do not display] the TTL . Use dig to Generate Condensed Output. Using the +short modifier after the dig command abbreviates the output of dig: $ dig example.com +short 207.192.72.27. You can combine the +short modifier with other dig commands to generate output that may be more useful in scripts as follows: $ dig mx example.com +short 10 mail.example.com.An underlined letter indicates a keyboard shortcut. Use it to (un)select the corresponding option. The shortcut for the "Dig" button is Q or Ctrl + Enter, for "Reset" it is 0, and for "Fix" it is X. Hovering over an option, you will get an explanation of the usage. The same can be done with TTLs and record types in the output.
The Linux dig command allows you to query DNS servers and perform DNS lookups. You can also find the domain an IP address leads back to. We'll show you how! How the dig Command Works People use the Linux dig . The dig command is a powerful tool for troubleshooting queries and responses received from the Domain Name Service (DNS). It is installed by default on many operating systems, including Linux® and Mac OS X. It can be . DIG Command dig (domain information groper) is a network administration CLI tool for querying DNS(Domain Name System) servers. dig is a very useful tool for troubleshooting network issues and can work in interactive command line mode or in batch mode. dig command is provided by bind package on RHEL/CentOS systems i.e. main DNS package. Dig .
Dig’s default output provides the TTL information, it is the number proceeding the record type (underlined below): $ dig +nocmd +noall +answer www.ateamsystems.com www.ateamsystems.com. 270 IN A 69.55.231.82 Note: If .QuinLED-Dig-Uno Pinout Guide Back to index page QuinLED-Dig-Uno v3 / v3.1 If you are looking for the QuinLED-Dig-Uno v2 pinout guide, please go here The GPIO_ESP32 number is what you use in WLED! LED1 and LED2 are only usable as outputs since the Level Shifter is unidirectional. The Dedicated GPIO’s are usable as inputs or [.]
I am using RFC 1035 as source, keeping to the sequence from there, regardless if you already mentioned it in your question.. QR specifies whether this message is a query (0), or a response (1) OPCODE A four bit field, only valid values: 0,1,2; AA Authoritative Answer Decoding dig output: +norecurse @nameserver MX to domain. Hot Network Questions python stats.spearmanr and R cor.test(method='spearman') don't return the same p-value? When a submarine blows its ballast and rises, where did the energy for the ascent come from? Are Experimental Elixirs Magic Items? .
dig output|10 Linux DIG Command Examples for DNS Lookup
PH0 · dig(1): DNS lookup utility
PH1 · dig Command in Linux with Examples
PH2 · Understanding Linux Dig Command
PH3 · Linux and Unix dig Command Examples
PH4 · How shall I understand the output of `dig`?
PH5 · Dig Command Examples in Linux
PH6 · Dig
PH7 · 10 Linux DIG Command Examples for DNS Lookup
PH8 · 10 Linux DIG Command Examples for DNS Lookup